Axial: https://linktr.ee/axialxyz
Axial partners with great founders and inventors. We invest in early-stage life sciences companies such as Appia Bio, Seranova Bio, Delix Therapeutics, Simcha Therapeutics, among others often when they are no more than an idea. We are fanatical about helping the rare inventor who is compelled to build their own enduring business. If you or someone you know has a great idea or company in life sciences, Axial would be excited to get to know you and possibly invest in your vision and company. We are excited to be in business with you — email us at info@axialvc.com
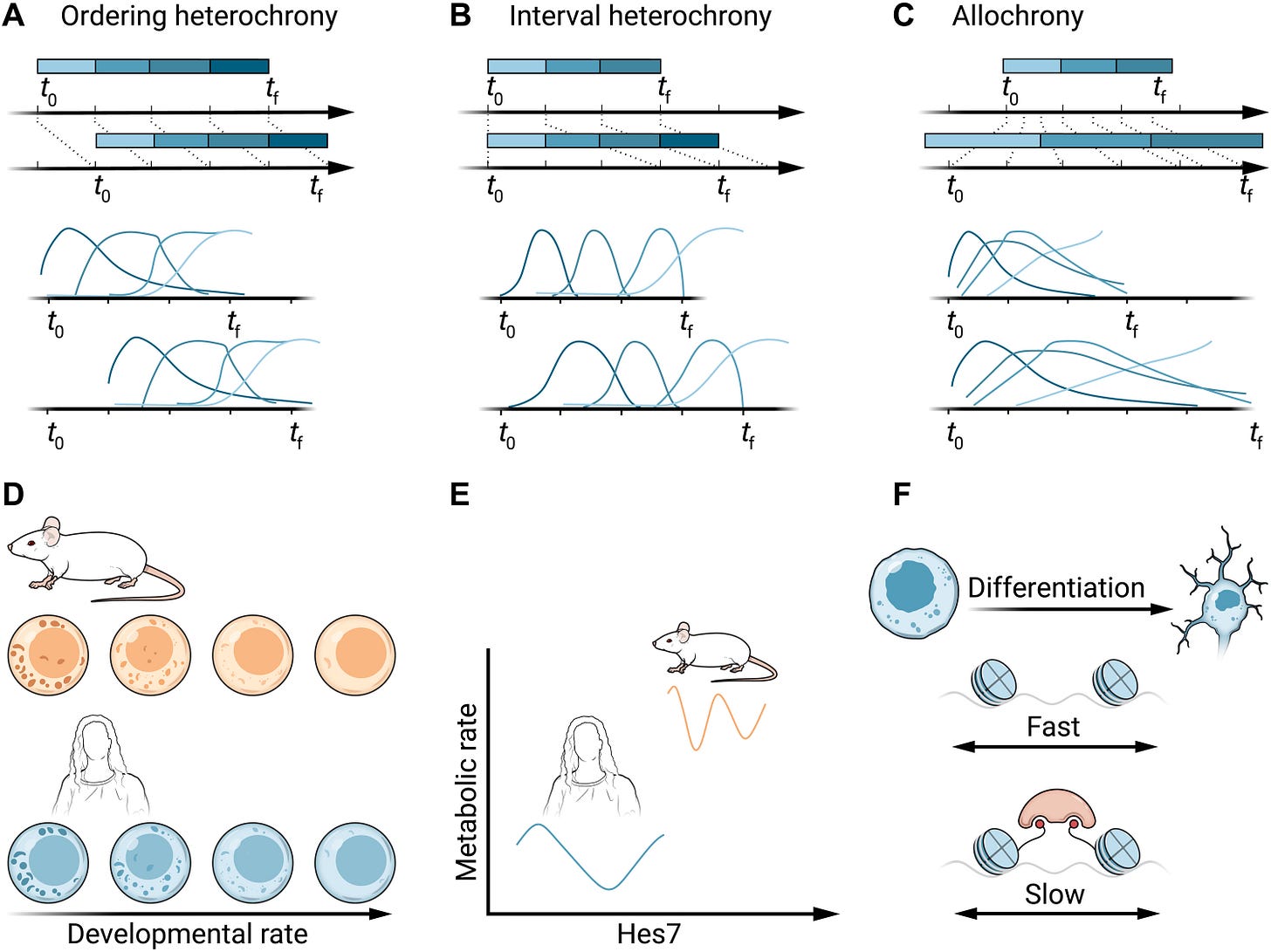
Biological timing is critical for development, involving the timing of initiation, duration, and rate/tempo of processes. Differences in timing across species are called heterochronies.
Cells contain intrinsic mechanisms that regulate developmental timing, even when isolated from embryonic cues and cell-cell interactions. Comparing timing in isolated cells from different species can reveal mechanisms behind heterochronies. The tempo of processes like somitogenesis and neurogenesis are 2-3x slower in human cells compared to mouse. This matches the slower overall gestation periods.
Differences in timing can arise from protein stability and degradation rates. Slower development associates with more stable proteins. Metabolic rate correlates with developmental tempo. Faster oscillations of segmentation genes occur in mouse cells with higher metabolic rates than human cells. Accelerating metabolism speeds up neuron maturation. Epigenetic regulation of gene expression can delay transitions in progenitor states during corticogenesis. Inhibiting repressive chromatin regulators accelerates neural differentiation.
While a few mechanisms have been identified, more work is needed to understand their relationships, conservation across tissues/species, and contributions to developmental heterochronies.