Borg extrachromosomal elements of methane-oxidizing archaea have conserved and expressed genetic repertoires
Inventors & their inventions
Axial: https://linktr.ee/axialxyz
Axial partners with great founders and inventors. We invest in early-stage life sciences companies such as Appia Bio, Seranova Bio, Delix Therapeutics, Simcha Therapeutics, among others often when they are no more than an idea. We are fanatical about helping the rare inventor who is compelled to build their own enduring business. If you or someone you know has a great idea or company in life sciences, Axial would be excited to get to know you and possibly invest in your vision and company . We are excited to be in business with you — email us at info@axialvc.com
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.08.01.549754v1.full.pdf
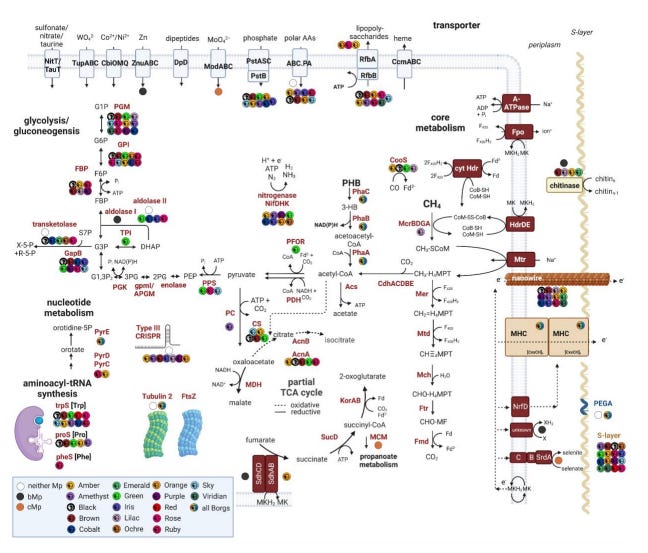
Borgs are huge extrachromosomal elements (ECE) of anaerobic methane-consuming archaea. They are up to 1.1 Mbp in length and have linear genomes terminated by kilobase-scale long inverted terminal repeats (ITR). The genes are encoded on two replichores of very uneven length, with essentially all genes on each replichore carried on a single strand.
They are predicted to replicate in Methanoperedens archaea based on sequence similarity, phylogeny, shared abundance-based co-occurrence patterns and CRISPR targeting. And were named “Borgs” because of their propensity to assimilate large numbers of genes from organisms, especially but not limited to their host Methanoperedens.
To date, their sequences have only been recovered from environmental metagenomic datasets from terrestrial subsurface ecosystems. The authors used long read sequences from Oxford Nanopore Technologies to validate the overall topologies of some of their short read-derived complete Borg genomes.
The paper also reconstructed additional complete and near-complete genomes. Finding that Borgs share a mostly syntenous set of conserved marker genes that could be used to identify new Borgs and define their phylogeny. They also found that Borgs have a high abundance of genes involved in anaerobic methane oxidation and nitrogen fixation. And may be capable of encapsulation.