Axial: https://linktr.ee/axialxyz
Axial partners with great founders and inventors. We invest in early-stage life sciences companies such as Appia Bio, Seranova Bio, Delix Therapeutics, Simcha Therapeutics, among others often when they are no more than an idea. We are fanatical about helping the rare inventor who is compelled to build their own enduring business. If you or someone you know has a great idea or company in life sciences, Axial would be excited to get to know you and possibly invest in your vision and company. We are excited to be in business with you — email us at info@axialvc.com
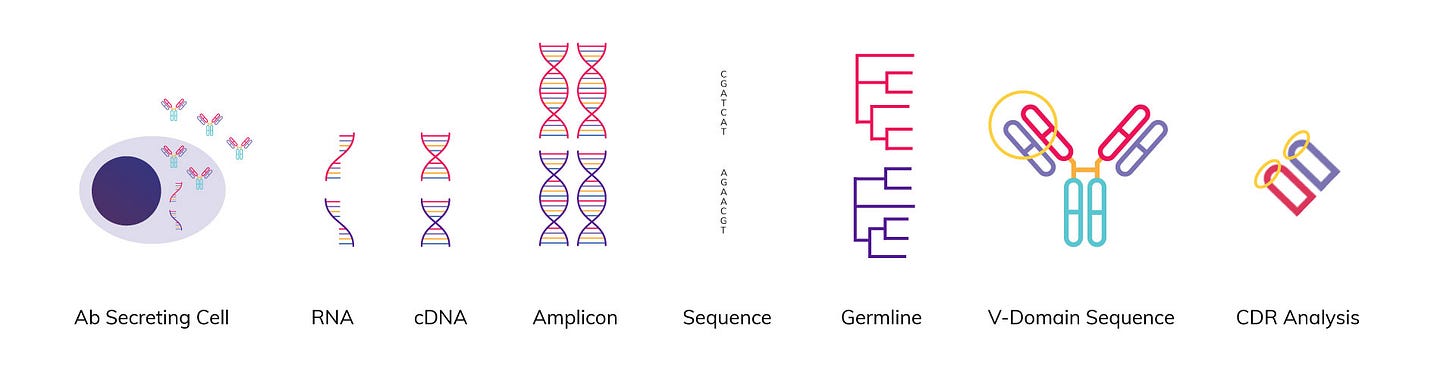
The ability to sequence antibodies while retaining the native pairing of heavy and light chains is critical for developing antibody-based drugs. Antibodies bind to antigens through their variable regions, which are composed of a variable heavy (VH) chain paired with a variable light (VL) chain. It is this VH/VL pair that determines an antibody's specificity and functionality against a given target.
However, traditional next-generation sequencing of antibody repertoires fails to retain linkage between VH and VL sequences. This means that even with deep sequencing, researchers end up with dissociated VH and VL sequence data. Without knowing the correct pairings, antibodies cannot be properly expressed, validated, or developed as candidate therapeutics.
New techniques can allow native VH/VL pairs to be resolved at scale using sequencing approaches. Emulsion encapsulation RT-PCR and molecular tagging with unique barcodes or UMIs enable tracing of heavy and light chain sequences back to their parent B-cells. Long-read sequencing can also produce reads spanning full-length VH and VL transcripts.
By using these methods, researchers can unlock huge antibody sequence databases with preserved specificity encoded by native VH/VL pairs. This allows high-throughput functional screening to identify rare, potent antibodies against therapeutic targets. Having sequence information linked to validated hits then speeds the antibody engineering and maturation process to optimize drug properties.
Overall, the ability to resolve native antibody pairs in NGS datasets unlocks critical capabilities for therapeutic discovery and development. It enables building diverse libraries covering vast epitope space for isolating antibodies against challenging antigens. And it accelerates hit triage and validation to rapidly hone clinical candidates. As these technologies continue advancing, native antibody sequencing promises to greatly expedite development of new antibody therapeutics.