An Fc engineering approach that modulates antibody-dependent cytokine release without altering cell-killing functions
Inventors & their inventions
Axial: https://linktr.ee/axialxyz
Axial partners with great founders and inventors. We invest in early-stage life sciences companies such as Appia Bio, Seranova Bio, Delix Therapeutics, Simcha Therapeutics, among others often when they are no more than an idea. We are fanatical about helping the rare inventor who is compelled to build their own enduring business. If you or someone you know has a great idea or company in life sciences, Axial would be excited to get to know you and possibly invest in your vision and company. We are excited to be in business with you — email us at info@axialvc.com
This research article investigates an Fc engineering approach for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that modulates antibody-dependent cytokine release (ADCR) without altering cell-killing functions. IgG1 mAbs elicited robust ADCC (antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity) and ADCR of proinflammatory cytokines like IFNγ, IL-1α, and IL-1β from peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). In contrast, IgG2 and IgG4 mAbs had limited ability to elicit these responses.
Macrophage-mediated ADCP (antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis) was elicited by IgG1, IgG2 and IgG4 mAbs. However, IgG1 and IgG4 also induced high levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and other cytokines like IL-8, MIP-1α, MIP-1β, and TNF. IgG2 induced ADCP but minimal cytokine release.
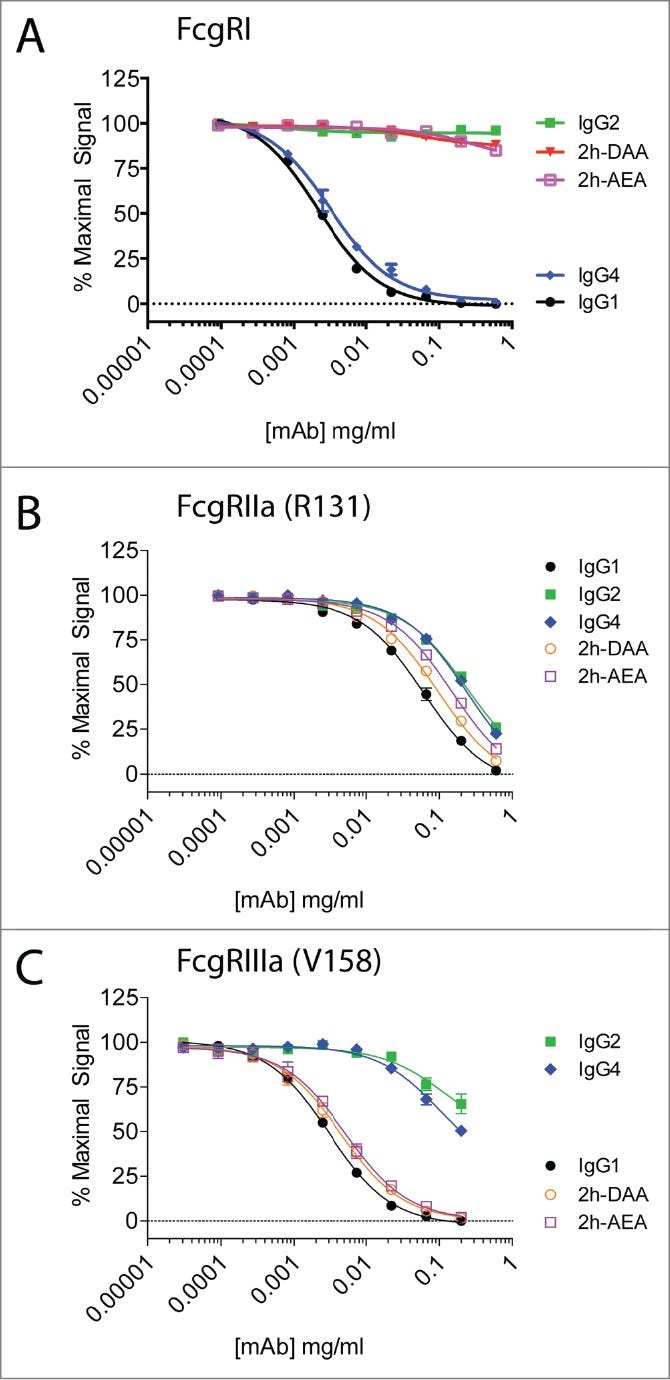
Engineered IgG1 variants 2h-DAA and 2h-AEA bound FcγRIIa and FcγRIIIa but not FcγRI. They elicited PBMC-mediated ADCC and proinflammatory cytokine release similarly to IgG1. However, they induced macrophage-mediated ADCP without cytokine release, unlike IgG1. The results suggest macrophage FcγRI engagement is critical for IL-10 and other cytokine induction. The engineered variants uncouple macrophage phagocytosis from cytokine release by selectively binding FcγRIIa/IIIa but not FcγRI.
This work demonstrates Fc engineering can modulate ADCR without altering cell-killing functions of mAbs. Isotype selection influences mAb functions beyond just cytotoxicity. IgG1 elicits proinflammatory cytokine release from PBMCs while IgG2/IgG4 do not. This shows considerations beyond just ADCC are important when selecting isotypes. The findings reveal new considerations for optimizing mAb therapies. Most Fc engineering focuses on improving cell-killing functions. But modulating ADCR may also be important. This study provides a proof-of-concept that engineering ADCR merits investigation for enhancing therapeutic efficacy.
In summary, this is an important study demonstrating isotype selection and Fc engineering can selectively modulate ADCR independently of cytotoxicity. The results suggest engineered variants selectively engaging FcγRs could help promote more favorable immune responses. This reveals new directions for optimizing mAb immunotherapies against cancer. The findings highlight the need to consider both cell-killing and broader immunomodulatory functions when designing mAbs. Overall, this study makes a significant contribution to understanding how mAb/FcγR interactions shape anti-tumor immunity and how this could be leveraged therapeutically through Fc engineering.